
Understanding the fossil record is crucial for researchers and scientists in tracking the history of life on Earth. By examining fossils, they are able to piece together the puzzle of the past and gain insights into the evolution of various organisms. To assist in this process, worksheets are often provided to students to help them analyze and interpret the information contained in the fossil record.
The fossil record worksheet answer key serves as a valuable resource for students as it provides the correct answers and explanations to the questions posed in the worksheet. It helps students understand how to identify fossils, interpret their significance, and make connections between different species and their evolutionary history.
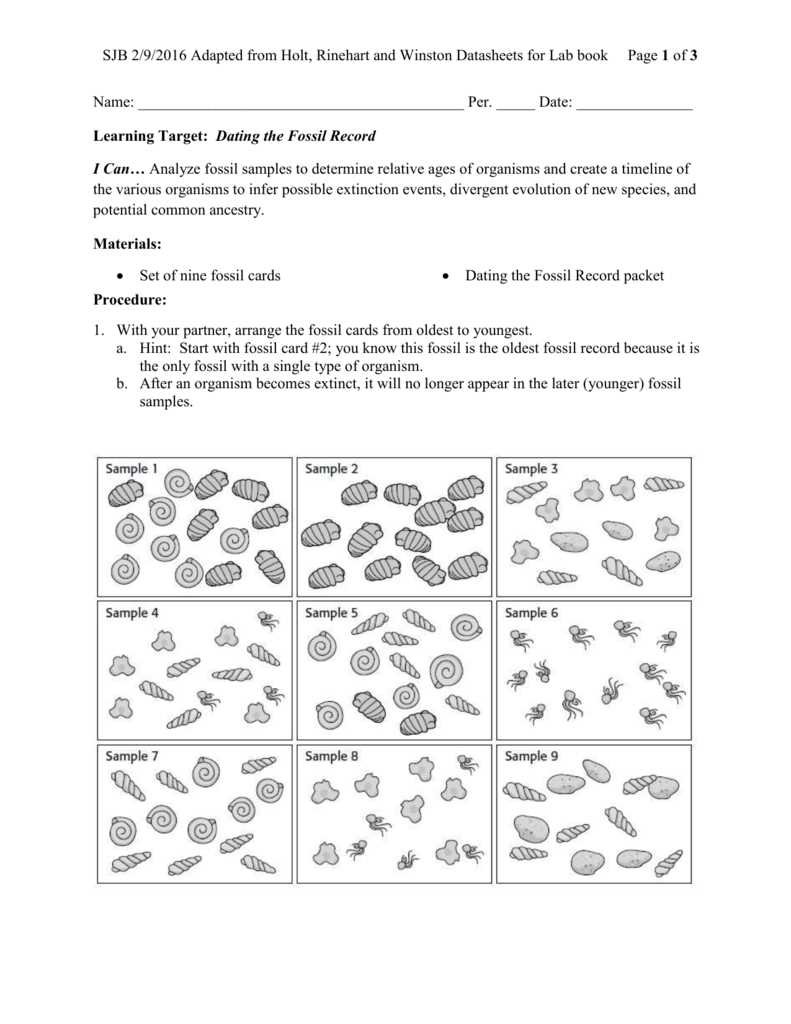
One of the key aspects of the fossil record worksheet is learning how to read and interpret data presented in various forms, such as fossil diagrams, stratigraphic columns, and timelines. The answer key provides examples and explanations on how to interpret these representations, enabling students to develop important skills in data analysis and visualization.
Additionally, the fossil record worksheet often includes questions that require students to think critically and apply their knowledge of evolutionary principles. The answer key not only provides the correct answers but also elaborates on the reasoning behind them, fostering a deeper understanding of the mechanisms that drive evolution.
In conclusion, the fossil record worksheet answer key is a vital tool that aids students in their understanding of the fossil record. It provides them with the necessary guidance and explanations to analyze and interpret the data presented in the worksheet. By mastering the skills and knowledge acquired through these worksheets, students can develop a solid foundation in paleontology and contribute to advancing our understanding of the history of life on Earth.
The Fossil Record Worksheet Answer Key: Unlocking the Secrets of Extinct Life
The Fossil Record Worksheet Answer Key is a valuable tool that allows students to uncover the mysteries of extinct life. By analyzing fossils, scientists have been able to reconstruct the history of life on Earth, providing important insights into the evolution and extinction of organisms. This answer key provides the necessary information and guidance to help students interpret and understand the fossil record, allowing them to unlock the secrets of the past.
The answer key begins by introducing students to the concept of fossils and explaining how they are formed. It highlights the different types of fossils, such as petrified, cast, and trace fossils, and explains how they provide evidence of past life. Students learn about the process of fossilization and understand the conditions necessary for the preservation of organisms in the fossil record.
The answer key then delves into the principles of relative dating and stratigraphy, which help scientists determine the age of fossils and their relative positions in the rock layers. Students learn how to interpret the information provided by the different layers of sedimentary rocks and how to use index fossils to establish the relative ages of different rock formations. They also explore the concept of radiometric dating, which allows for the absolute dating of fossils based on the decay of radioactive isotopes.
The answer key further explores the concept of evolutionary change through the examination of fossil evidence. Students learn about transitional fossils, which provide evidence of intermediate forms between different species, and how they support the theory of evolution. They also explore the notion of extinction and how the fossil record helps us understand the processes and patterns of extinction throughout Earth’s history.
Overall, the Fossil Record Worksheet Answer Key serves as a comprehensive guide for students to navigate and understand the fossil record. It empowers them to unlock the secrets of extinct life by analyzing fossils and understanding their significance in the context of Earth’s history. By providing the necessary information and guidance, the answer key facilitates learning and helps students develop a deeper appreciation for the wonders of the fossil record.
Understanding the Fossil Record: A Comprehensive Overview

The fossil record is a crucial tool for scientists to understand the history of life on Earth. It provides important evidence of the existence and evolution of different species over millions of years. By studying the fossil record, scientists can gain insights into the characteristics, behaviors, and relationships of ancient organisms. This information helps to fill gaps in our knowledge about the past, and allows us to make connections between extinct species and their living counterparts.
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms. They can include bones, teeth, shells, imprints, and even traces of soft tissues. Fossils are typically found in sedimentary rock, which forms when layers of sediment accumulate over time. By carefully studying the location and characteristics of fossils within these rock layers, scientists can determine their age and the environment in which they lived.
The fossil record is divided into different time periods, known as geological eras, which provide a timeline of Earth’s history. The three main eras are the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic. Each era is further divided into periods, such as the Jurassic or the Carboniferous. These divisions allow scientists to compare and analyze different organisms and ecosystems that existed during specific time periods.
One of the key concepts in understanding the fossil record is the principle of faunal succession. This principle states that fossils found in rock layers can be used to determine the relative age of those layers. It is based on the observation that certain types of organisms existed only during specific time periods. By comparing the fossils found in different rock layers, scientists can determine the order in which these layers were formed and the sequence of events in Earth’s history.
Overall, the fossil record provides a wealth of information about the history of life on Earth. It allows scientists to reconstruct ancient ecosystems, study extinct species, and gain insights into the processes of evolution and adaptation. By continuing to study and analyze the fossil record, scientists can uncover even more secrets about the past and deepen our understanding of the natural world.
Exploring Fossil Types: From Imprints to Petrified Remains
The fossil record provides an invaluable glimpse into the history of life on Earth, offering a window into the past that allows scientists to study and understand ancient organisms. Fossils come in various types, each with its own unique characteristics and preservation. From imprints to petrified remains, the diverse range of fossils offers insights into the biology, behavior, and environments of long-extinct species.
Imprints, also known as trace fossils, are impressions left behind by ancient organisms. These fossils can include footprints, burrows, and feces. The imprints provide evidence of the presence and activities of organisms that may not have been preserved as body fossils. Through the study of imprints, paleontologists can reconstruct the behavior and locomotion of ancient species, revealing valuable information about their lives and interactions.
Body fossils, on the other hand, are the remains of actual organisms that have been preserved. These fossils can be further classified into several different types based on their composition. Petrified remains, for example, are formed when organic material is gradually replaced by minerals, turning the remains into stone. This process preserves the structure and fine details of the organism, allowing scientists to study its anatomy and make inferences about its evolutionary relationships.
In addition to petrification, other forms of fossilization can occur, such as carbonization and permineralization. Carbonization happens when an organism is preserved in a thin layer of carbon, which forms a dark imprint of the organism’s body. Permineralization, on the other hand, occurs when the organism’s remains are infiltrated by minerals, filling the pores and preserving the original structure. These different types of fossilization provide unique insights into the past, offering glimpses into the diversity of ancient life and the environmental conditions in which it thrived.
- Imprints, or trace fossils, provide evidence of the presence and activities of ancient organisms.
- Petrified remains, formed through the gradual replacement of organic material by minerals, preserve the structure and anatomy of ancient organisms.
- Carbonization and permineralization are other forms of fossilization, each with its own distinct characteristics and preservation.
The fossil record, with its wide array of fossil types, continues to enhance our understanding of the history of life on Earth. Through the study of imprints, petrified remains, and other fossil types, scientists can piece together the puzzle of past ecosystems and uncover the secrets of extinct species. From the tiniest trilobites to the majestic dinosaurs, fossils tell the story of life’s evolution and adaptation over millions of years.
Interpreting Fossil Age: How Geologists Determine Earth’s Timeline
The fossil record provides important evidence of Earth’s history and the evolution of life on our planet. Geologists use various methods to determine the age of fossils and establish a timeline of Earth’s geological events. By analyzing the different layers of rock and fossilized remains, scientists can piece together the past and gain insights into the origins and development of life.
One crucial method used by geologists to determine fossil age is relative dating. This technique involves comparing the age of one rock layer or fossil to another, using principles such as superposition and cross-cutting relationships. By examining the sequence of layers in a rock formation, scientists can determine the relative age of fossils found within those layers. For example, if a fossil is found in a deeper layer of rock, it is likely older than a fossil found in a higher layer.
Another method used to interpret fossil age is radiometric dating, which relies on the decay of radioactive isotopes. This technique measures the ratio of parent isotopes to daughter isotopes in a rock sample to determine its absolute age. By knowing the half-life of a particular radioactive isotope, scientists can calculate how long it has been since the rock or fossil formed. This method is particularly useful for dating rocks and fossils that are millions or billions of years old.
In addition to these dating techniques, paleontologists also consider the index fossils found in specific rock layers. Index fossils are species that existed for a relatively short period but were widespread geographically. By identifying and dating these index fossils, scientists can correlate the ages of different rock formations and create a more detailed timeline of Earth’s history. These index fossils serve as key indicators of specific time periods and help determine the age of other fossils found in the same layer.
In conclusion, geologists use a combination of relative dating, radiometric dating, and the presence of index fossils to interpret the age of fossils and establish Earth’s timeline. By studying the layers of rock and analyzing the fossil record, scientists can reconstruct the past and gain valuable insights into the history of life on our planet.
The Significance of Fossils in Evolutionary Studies
Fossils play a crucial role in understanding the process of evolution and the history of life on Earth. They are the preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms that lived millions of years ago. Through the study of fossils, scientists are able to reconstruct the evolutionary history of different species and understand how they have changed over time.
One of the key importance of fossils in evolutionary studies is their ability to provide direct evidence of past life forms. Fossils serve as a time capsule, preserving the remains of organisms that have long gone extinct. By analyzing these fossils, scientists can determine the characteristics and traits of ancient organisms, allowing them to trace the evolutionary relationships between different species and reconstruct the past ecosystems.
Fossils also provide important insights into the process of natural selection and adaptation. By studying the fossil record, scientists can observe how organisms have evolved and adapted to their environments over millions of years. They can track the gradual changes in the morphology, behavior, and ecology of species, and identify key transitional forms that provide evidence for the occurrence of evolutionary processes.
Furthermore, fossils help to fill in gaps in the evolutionary history of different species. As not all organisms fossilize, there are often significant gaps in the fossil record. However, the fossils that have been discovered provide valuable evidence for understanding the origins and evolution of various groups of organisms. By piecing together the puzzle of fossil evidence, scientists can build a more comprehensive picture of the diversity and evolutionary relationships of different species.
In conclusion, fossils are essential in evolutionary studies as they provide direct evidence of past life forms, offer insights into the process of natural selection and adaptation, and help to fill in gaps in the evolutionary history of species. By studying fossils, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the history of life on Earth and the processes that have shaped the diversity of species we see today.
Unlocking Ancient Climate with Fossil Evidence
The fossil record provides valuable clues about Earth’s ancient climate and allows scientists to reconstruct past environmental conditions. By studying fossils and their distribution, scientists can gain insights into the temperature, precipitation, and even the composition of the atmosphere during different periods of Earth’s history. Fossils serve as a window into the past, preserving the remains of ancient organisms and their surrounding environment.
One way scientists analyze the fossil record to unlock ancient climate is by studying the types of organisms that lived during a particular time period. Different plants and animals have specific environmental requirements, such as temperature and moisture levels, which determine their distribution. By examining the fossils of these organisms, scientists can infer the climatic conditions in which they thrived or went extinct. For example, the presence of certain plant species, like ferns or palm trees, can indicate a warm and humid climate, while the presence of certain marine fossils can provide evidence of ancient sea levels.
Another method used to unlock ancient climate with fossil evidence is the examination of stable isotopes. Isotopes are variations of elements with different numbers of neutrons but the same number of protons. Different isotopes can react to environmental conditions differently, and their ratio can provide information about past climate. By analyzing the isotopic composition of fossilized organisms, such as shells or bones, scientists can determine factors like temperature, salinity, and precipitation patterns. This information helps reconstruct the climatic conditions that prevailed millions of years ago.
Additionally, the study of pollen and spores, known as palynology, is another powerful tool for unlocking ancient climate. Pollen grains and spores are tiny, durable structures produced by plants. They are released into the environment and, under favorable conditions, are preserved in sediment layers. By analyzing the abundance and diversity of pollen and spore types in fossil records, scientists can reconstruct past vegetation patterns and infer climate. Pollen analysis can provide insights into temperature, precipitation, and even changes in plant communities over time.
In conclusion, the fossil record is not only a record of ancient life but also a treasure trove of information about Earth’s climatic history. Through the analysis of fossils, stable isotopes, and pollen records, scientists can unlock the secrets of past climates, revealing how our planet has changed over millions of years. This knowledge is crucial for understanding current climate change and predicting future climate scenarios.
Using the Fossil Record to Piece Together Earth’s Past Ecosystems

The fossil record is a valuable tool for scientists to understand and piece together Earth’s past ecosystems. By studying the remains of ancient organisms, scientists can gain insights into the diversity, structure, and interactions of past ecosystems. This information is crucial for understanding the history of life on Earth and how it has shaped our planet.
1. Studying Fossilized Plants and Animals:
Through the fossil record, scientists can examine the fossilized remains of plants and animals that lived millions of years ago. By analyzing these fossils, they can determine the types of organisms that lived in specific regions and their relationships to one another. This allows them to reconstruct the composition and structure of past ecosystems.
2. Tracking Environmental Changes:
Fossils also provide evidence of past environmental changes. By studying the distribution of fossilized organisms and their adaptations, scientists can infer information about ancient climates, habitats, and ecosystems. This data helps them understand how these ecosystems responded and adapted to environmental changes, such as climate shifts or the emergence of new geological features.
3. Piecing Together Food Webs and Trophic Interactions:
The fossil record allows scientists to reconstruct ancient food webs and trophic interactions. By analyzing the fossilized remains of predators, prey, and their associated species, scientists can unravel complex relationships and dynamics within past ecosystems. This information provides insights into the flow of energy and matter, and how the loss or introduction of certain species can impact the balance and stability of ecosystems.
4. Understanding Biodiversity and Extinction Events:
Fossils record the history of biodiversity on Earth. By examining the abundance and diversity of fossilized organisms over time, scientists can identify patterns and trends in biodiversity. They can also study mass extinction events and their aftermaths, shedding light on the factors that have influenced the rise and fall of different species and ecosystems throughout Earth’s history.
Conclusion:
The fossil record is an indispensable tool for understanding and reconstructing Earth’s past ecosystems. Through the study of fossilized plants and animals, tracking environmental changes, piecing together food webs and trophic interactions, and understanding biodiversity and extinction events, scientists can gain profound insights into the history and dynamics of our planet’s ecosystems. This knowledge is crucial for informing our understanding of the present and future of Earth’s biodiversity and ecosystems, and for guiding conservation efforts to protect the fragile balance of life on our planet.