Urbanization and immigration have been closely intertwined throughout history, shaping not only the physical landscape of cities but also the social and cultural fabric of communities. As people flocked to cities in search of economic opportunities, cities became centers of diverse cultures and melting pots of different languages and traditions. This document-based questions (DBQ) answers key aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the impacts of urbanization and immigration on society.
One of the main consequences of urbanization and immigration was the rapid growth of cities. As industries flourished and job opportunities arose, rural populations migrated to urban areas in large numbers. This influx of people created overcrowding, poor living conditions, and strained resources in cities. However, it also resulted in the establishment of vibrant neighborhoods and the development of new urban infrastructure.
Another significant aspect of urbanization and immigration was the transformation of city demographics. Immigrants from different countries and regions brought with them their unique cultures, customs, and languages, enriching the cultural tapestry of cities. However, the presence of diverse communities also gave rise to social tensions and discrimination, as native-born residents often viewed immigrants as competition for jobs and resources.
This DBQ answers key will delve into primary source documents from the time period to analyze the various reactions and responses to urbanization and immigration. By examining these historical documents, readers will gain insight into how governments, organizations, and individuals addressed the challenges and opportunities brought about by these processes. Ultimately, this DBQ answers key aims to shed light on the complex and multifaceted impact of urbanization and immigration on society and to encourage critical thinking and analysis of historical sources.
Urbanization and Immigration Document Based Questions Answers Key
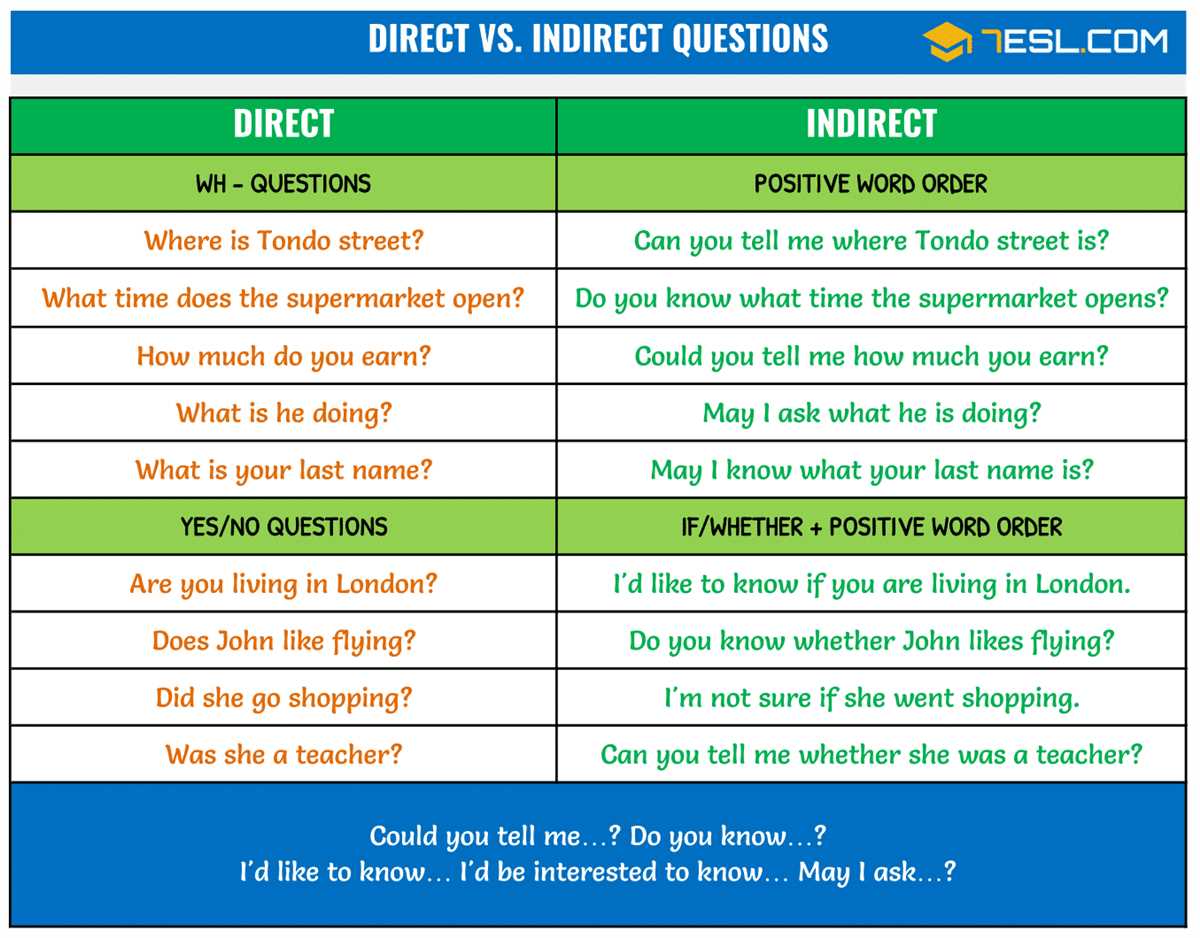
Urbanization and immigration were key factors in the growth and development of the United States in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. As the country experienced rapid industrialization and technological advancements, urban areas became centers of economic activity and drew in a large number of immigrants from various parts of the world. This document based question answers key aims to explore the impact and challenges of urbanization and immigration during this period.
One of the key documents that sheds light on the challenges of urbanization and immigration is the Tenement House Act of 1901. This act was passed in response to the overcrowded and unsanitary living conditions in urban tenements. It required landlords to provide better living conditions, such as proper ventilation and lighting, and limited the number of occupants per room. This document highlights the dire living conditions that many immigrants and lower-income individuals faced in urban areas and the efforts made to improve their living conditions.
Another document that provides insight into the impact of immigration and urbanization is The New York City Map from 1870. This map shows the rapid growth of the city during this time period, with the population increasing from around 1.5 million in 1860 to over 3.4 million in 1870. The map also indicates the locations of immigrant neighborhoods, such as Little Italy and Chinatown, demonstrating the clustering of various immigrant groups in specific areas of the city. This document underscores the significant role that immigration played in shaping the demographics and cultural landscape of urban areas in the United States.
- underline
- Format text
- Numbered list
- Another item
In conclusion, urbanization and immigration had a profound impact on the growth and development of the United States during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. These processes led to the rapid expansion of cities, the influx of immigrants from diverse backgrounds, and the emergence of distinct immigrant communities within urban areas. The challenges of urbanization, such as overcrowded and unsanitary living conditions, were addressed through legislation like the Tenement House Act of 1901. The rapid growth of cities and the clustering of immigrant groups in specific neighborhoods is evident in documents like The New York City Map from 1870. Overall, these documents provide valuable insights into the historical significance of urbanization and immigration in shaping the United States during this time period.
Overview

Urbanization and immigration were two significant phenomena that reshaped American society in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The rapid industrialization and urbanization brought about a massive influx of immigrants, particularly from Southern and Eastern Europe. These immigrants were drawn to America’s expanding industrial sector and sought better economic opportunities. However, the process of urbanization also led to various social, economic, and political challenges.
The growth of cities during this period was unprecedented. People flocked to urban areas in search of jobs and better living conditions, resulting in overcrowded cities with limited resources and inadequate infrastructure. This rapid population growth and urbanization led to the emergence of slums and tenement housing, where many immigrants and low-wage workers lived in deplorable conditions.
The influx of immigrants also brought about cultural and ethnic diversity to American cities. Different immigrant groups settled in specific neighborhoods, forming ethnic enclaves where they could maintain their customs, language, and traditions. This diversity, however, also led to tensions and conflicts between different ethnic groups, as well as between the immigrants and the established American population.
Furthermore, urbanization and immigration raised concerns about social issues and public health. The influx of immigrants, combined with poor living conditions and sanitation, contributed to the spread of diseases such as tuberculosis and cholera. Authorities struggled to provide adequate healthcare and sanitation infrastructure to address these concerns.
In conclusion, urbanization and immigration during the late 19th and early 20th centuries brought about significant changes in American society. While immigrants sought better economic opportunities, the rapid urbanization resulted in overcrowded cities, housing crises, and social tensions. The impact of urbanization and immigration on American society is still felt today, shaping the country’s cultural, social, and economic landscape.
Understanding Urbanization
Urbanization is the process of population shift from rural areas to urban areas, resulting in the growth and expansion of cities. It is driven by various factors such as industrialization, economic development, and immigration. This phenomenon has significant effects on the social, economic, and environmental aspects of a society, and it is important to understand its implications.
One of the key factors driving urbanization is industrialization. As industries develop and expand, there is a need for a larger workforce, which leads to increased migration from rural areas to urban centers. This influx of people seeking employment opportunities often results in the rapid expansion of cities, as new housing, infrastructure, and services need to be built to accommodate the growing population.
Moreover, urbanization is closely linked to economic development. Cities have historically been centers of commerce, trade, and innovation, attracting businesses and entrepreneurs. The concentration of economic activities in urban areas leads to job creation and increased opportunities for individuals. However, it also creates challenges such as income inequality and overcrowding, as the demand for resources and services often exceeds the supply.
Immigration is another significant factor contributing to urbanization. People often migrate from rural areas or other countries in search of better living conditions, education, and employment opportunities. Immigration can bring cultural diversity and contribute to the growth and dynamism of urban areas. However, it also poses challenges in terms of infrastructure and social integration.
In conclusion, urbanization is a complex process that involves the shift of population from rural areas to urban areas. It is driven by factors such as industrialization, economic development, and immigration. Understanding the implications of urbanization is essential for policymakers to ensure sustainable urban growth and address the challenges it poses in areas such as housing, infrastructure, and social inequality.
Causes of Urbanization
The process of urbanization, or the growth and expansion of cities, was primarily driven by a combination of factors during the 19th and 20th centuries. Industrialization, improved transportation, and population growth were key catalysts behind this urban phenomenon.
1. Industrialization: The rise of industrialization played a significant role in the urbanization process. The development of factories and the shift from manual labor to mass production led to an increase in job opportunities in cities. Many rural individuals migrated to urban areas in search of employment in factories and industries, which fueled the population growth in cities.
2. Improved Transportation: The advancement in transportation infrastructure, such as the construction of railroads and canals, facilitated the movement of people and goods between rural and urban areas. The availability of faster and more efficient modes of transportation made it easier for individuals to commute to cities for work and trade. This accessibility further encouraged the migration of people towards urban centers.
3. Population Growth: The overall population growth during this period also contributed to urbanization. As the population increased, the demand for housing, services, and amenities also grew. Cities could provide these resources more effectively due to economies of scale. Moreover, the concentration of people in cities led to the development of various cultural, social, and educational institutions, attracting more individuals to urban areas.
In conclusion, industrialization, improved transportation, and population growth were significant causes of urbanization. These factors worked together to transform rural areas into bustling urban centers, driving the migration of people towards cities in search of employment, opportunities, and better living conditions.
Impacts of Urbanization
Urbanization, the process of population concentration in cities, has had significant impacts on societies and economies around the world. As rural populations move to urban areas in search of better opportunities, the landscape of cities undergoes profound changes that affect various aspects of life for both individuals and communities.
Growth of cities: One of the most notable impacts of urbanization is the rapid growth of cities. Formerly small towns or villages may quickly transform into bustling metropolises, as the influx of people leads to an expansion of infrastructure, housing, and services. This growth can bring both advantages and challenges, as cities strive to accommodate and provide for their growing populations.
Economic development: Urbanization is often associated with economic development, as cities become centers of industry, commerce, and innovation. Urban areas attract businesses and investment, creating job opportunities and driving economic growth. The concentration of people in cities also facilitates the exchange of ideas and knowledge, fostering innovation and technological advancement.
Social and cultural changes: The process of urbanization can lead to significant social and cultural changes within communities. As people from different backgrounds and regions converge in cities, cultural diversity increases, and new social networks and communities emerge. Urban areas become melting pots of different traditions, languages, and customs, contributing to a vibrant and dynamic cultural scene.
Challenges of urbanization: While urbanization brings numerous benefits, it also poses challenges that require careful planning and management. Rapid population growth can strain resources and infrastructure, leading to issues like overcrowding, inadequate housing, and increased pollution. Furthermore, urbanization can contribute to income inequalities and social disparities, as not all individuals are able to benefit equally from the opportunities offered by urban areas.
In conclusion, urbanization has far-reaching effects on societies and economies. It transforms landscapes, fosters economic growth, brings about social and cultural changes, and presents challenges that need to be addressed for sustainable urban development.
Understanding Immigration
Immigration is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that has shaped societies throughout history. It refers to the movement of people from one country to another with the intention of settling permanently. The reasons for immigration vary, but they often include economic opportunities, political instability, and social factors. Understanding the motivations behind immigration is crucial in order to address the challenges and opportunities associated with it effectively.
One key factor that drives immigration is the pursuit of better economic prospects. People may choose to leave their home countries in search of higher wages, job opportunities, and improved living standards. This economic-driven migration has been fueled by globalization, which has increased the mobility of capital and the demand for labor in certain industries and regions. Immigration can have both positive and negative impacts on receiving countries’ economies, and understanding the economic benefits and costs is essential for policy-making.
Political and social factors also play a significant role in driving immigration. Political instability, conflict, and persecution in home countries can force individuals and families to seek safety and security elsewhere. Additionally, social factors such as family reunification and educational opportunities can also influence the decision to immigrate. Understanding these factors is crucial for designing policies that address the needs and rights of refugees and asylum seekers.
In conclusion, immigration is a complex and diverse phenomenon that should be understood from multiple perspectives. By understanding the economic, political, and social motivations behind immigration, societies can develop policies and practices that can maximize its positive impacts and address the challenges associated with it effectively.
Impacts of Immigration on Urbanization

Immigration has had a significant impact on urbanization throughout history. The movement of people from rural areas to cities has led to rapid population growth in urban centers. This has resulted in a range of social, economic, and cultural changes that have shaped the development of cities.
One of the key impacts of immigration on urbanization is the diversity it brings to cities. Immigrants often come from different countries and bring with them their own languages, customs, and traditions. This diversity enriches the cultural fabric of cities and contributes to their vibrant and multicultural nature.
Economic impacts:
- Immigrants have played a vital role in labor markets and have filled gaps in the workforce, particularly in industries with low-skilled jobs.
- They have contributed to economic growth by starting businesses and creating jobs.
- Immigrants have also been consumers, stimulating local economies and contributing to the overall economic development of cities.
Social impacts:
- Immigrants have contributed to the population growth of urban areas, leading to increased diversity and cultural exchange.
- They have brought new ideas, skills, and perspectives, which have enriched the social fabric of cities.
- However, immigration has also led to social tensions and conflicts, particularly in periods of economic uncertainty or when cultural differences are not effectively managed.
Infrastructure impacts:
- Immigration has put pressure on urban infrastructure, such as housing, transportation, and public services.
- Cities have had to expand and invest in infrastructure to accommodate the growing population.
- This has sometimes led to overcrowding, strained resources, and increased inequality within cities.
In conclusion, immigration has been a significant factor in shaping the process of urbanization. It has brought diversity, contributed to economic growth, and enriched the social fabric of cities. However, it has also presented challenges in terms of infrastructure and social cohesion. Effective management of immigration is crucial to ensure the positive impacts outweigh the negative ones and to foster inclusive and sustainable urban development.