Triangles are a fundamental shape in geometry, and they come in various forms. But have you ever wondered which types of triangles are the coldest? In this worksheet, we will explore different types of triangles and their characteristics to find out which ones generate the least amount of heat.
To determine the coldest triangles, we need to consider their properties such as angles and side lengths. One significant characteristic is the presence of right angles. Right triangles have one angle equal to 90 degrees, which means they have one side perpendicular to another. This perpendicular side can minimize heat transfer, making right triangles potentially colder than other types.
Another factor to consider is the length of the sides. Equilateral triangles, for example, have three equal side lengths and three equal angles. Due to their symmetry, they tend to distribute heat evenly, which may result in a more balanced temperature. On the other hand, scalene triangles have no equal sides or angles, and their uneven distribution of heat could potentially make them colder in specific areas.
In conclusion, right triangles and scalene triangles are the types of triangles that could potentially be the coldest. The presence of right angles in right triangles and the uneven distribution of heat in scalene triangles make them unique candidates for generating the least amount of heat. This worksheet will further explore these ideas and provide answers to the question, “What kinds of triangles are the coldest?”
The Importance of Knowing Types of Triangles in Mathematics
Understanding the different types of triangles is an essential part of learning mathematics. Triangles are one of the fundamental shapes in geometry, and their properties and characteristics can be used to solve various mathematical problems. By knowing the types of triangles and their specific attributes, students can apply mathematical concepts more effectively and solve problems more efficiently.
One of the key benefits of knowing the types of triangles is the ability to classify and identify them correctly. Triangles can be classified based on their angles (acute, obtuse, or right) and their sides (equilateral, isosceles, or scalene). By understanding these classifications, students can accurately describe and categorize triangles, which is essential for clear communication in mathematics. Additionally, knowing the types of triangles helps in identifying patterns and relationships between different triangles, enabling students to make connections and solve more complex problems.
Knowing the types of triangles also helps in solving geometric equations and proofs. For example, when solving equations involving triangle angles, the knowledge of different types of triangles assists in determining the unknown angles and applying relevant theorems or formulas. Similarly, when constructing geometric proofs, understanding the properties of triangles allows students to choose the appropriate postulates or theorems to justify their reasoning.
Furthermore, identifying and understanding types of triangles is important when working with real-world applications of mathematics. Many practical scenarios, such as construction, architecture, and engineering, involve the use of triangles. By recognizing the types of triangles involved in these contexts, students can apply mathematical concepts to calculate measurements, angles, and proportions, ensuring accuracy and precision in their calculations.
In conclusion, knowing the types of triangles is crucial in mathematics as it allows for accurate classification, problem-solving, equation-solving, geometric proofs, and real-world applications. It enhances students’ overall understanding of geometry and provides them with a solid foundation for further mathematical studies and problem-solving skills.
Why understanding different types of triangles is crucial in mathematics
In mathematics, triangles are a fundamental shape that is studied extensively. Understanding the different types of triangles is crucial because it allows mathematicians to classify and analyze various geometrical properties. Triangles play a significant role in various mathematical fields, such as geometry, trigonometry, and algebra.
One of the most basic classifications of triangles is based on their sides. Equilateral triangles have three equal sides, isosceles triangles have two equal sides, and scalene triangles have no equal sides. This categorization helps mathematicians analyze and solve problems related to symmetry, congruence, and similarity. For example, equilateral triangles have rotational symmetry and can be used to create tessellations.
Another important classification of triangles is based on their angles. Right triangles have one 90-degree angle, acute triangles have three angles less than 90 degrees, and obtuse triangles have one angle greater than 90 degrees. This classification is crucial in trigonometry, as it helps in calculating trigonometric ratios such as sine, cosine, and tangent. Right triangles, in particular, are significant in the Pythagorean theorem and applications of trigonometry in real-world problems.
The study of triangles also involves exploring relationships between their sides and angles. For example, the Law of Sines and the Law of Cosines are formulas that describe the relationship between the angles and sides of a triangle. These formulas are essential in solving problems involving triangles, such as finding unknown side lengths or angles in trigonometric equations.
Overall, understanding the different types of triangles is crucial in mathematics because it provides a foundation for analyzing and solving various geometric and trigonometric problems. Triangles serve as building blocks for more complex shapes, and their properties have applications in diverse fields such as architecture, engineering, and computer graphics. By mastering the concepts of triangles, mathematicians can unravel intricate mathematical problems and explore the beauty of geometry.
Identifying and Classifying Triangles
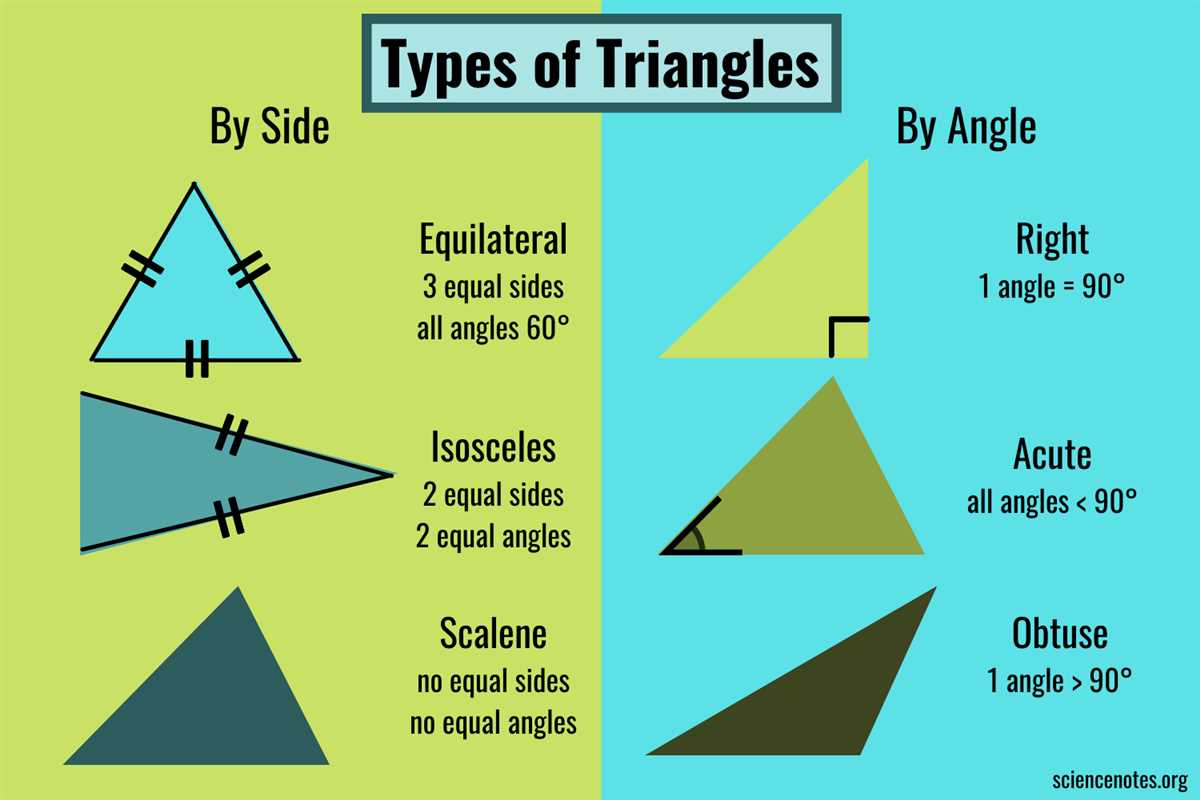
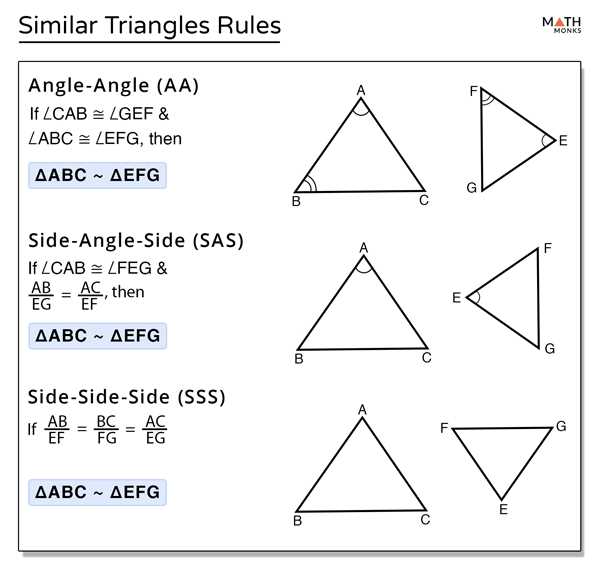
In geometry, a triangle is a polygon with three sides and three angles. Triangles can be classified based on several different characteristics, including the measure of their angles and the length of their sides. By understanding these characteristics, we can identify and classify triangles.
One way to classify triangles is by the measure of their angles. An acute triangle is a triangle in which all three angles are less than 90 degrees. A right triangle is a triangle that has one angle measuring exactly 90 degrees. An obtuse triangle is a triangle with one angle greater than 90 degrees. These classifications are important in understanding the properties and relationships of different triangles.
Another way to classify triangles is by the length of their sides. An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides are equal in length. A scalene triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have different lengths. A isosceles triangle is a triangle in which two sides are equal in length, and the third side is different. These classifications are useful in determining the symmetry and balance of different triangles.
By identifying and classifying triangles based on their angles and sides, we can better understand the properties and characteristics of triangles. This knowledge is important in various areas of mathematics and can be applied to real-life situations, such as construction and architecture.
How to identify and classify various types of triangles

Triangles are three-sided polygons that are widely studied and classified in geometry. Understanding the different types of triangles is essential for geometry students, as it helps them solve problems and apply theorems related to triangles. Here, we will discuss how to identify and classify various types of triangles based on their sides and angles.
Classifying triangles based on sides:
Triangles can be classified based on the lengths of their sides. The three main types of triangles based on sides are:
- Equilateral triangle: An equilateral triangle has all three sides of equal length. This means that all three angles of an equilateral triangle are also equal, measuring 60 degrees each.
- Isosceles triangle: An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. The angles opposite the equal sides are also equal.
- Scalene triangle: A scalene triangle has three sides of different lengths. None of the angles in a scalene triangle are equal.
Classifying triangles based on angles:

Triangles can also be classified based on the measures of their angles. The three main types of triangles based on angles are:
- Acute triangle: An acute triangle has all three angles measuring less than 90 degrees.
- Right triangle: A right triangle has one angle measuring exactly 90 degrees. The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
- Obtuse triangle: An obtuse triangle has one angle measuring more than 90 degrees.
By analyzing the lengths of the sides and the measures of the angles, it is possible to identify and classify triangles accurately. This knowledge is useful in various areas such as engineering, architecture, and construction, where precise triangle classification is crucial for designing structures.
Exploring the Properties of Equilateral Triangles
Equilateral triangles are a special type of triangle that have unique properties. These triangles have three equal sides and three equal angles, each measuring 60 degrees. The symmetry of an equilateral triangle makes it an interesting shape to study and explore.
Side Lengths: One of the key properties of equilateral triangles is that all three sides are the same length. This means that if you know the length of one side, you automatically know the lengths of the other two sides. This property is helpful in solving various mathematical problems involving equilateral triangles.
Angles: All three angles in an equilateral triangle are congruent and measure 60 degrees each. This property makes equilateral triangles useful in various geometric calculations and constructions. For example, the angles in an equilateral triangle can be used to create larger polygons and determine the angles of intersections between lines.
Properties of Equilateral Triangles:
- All three sides are the same length.
- All three angles measure 60 degrees.
- The sum of the angles in an equilateral triangle is always 180 degrees.
Area: The area of an equilateral triangle can be calculated using the formula A = (s^2 * √3) / 4, where s is the length of one side. This formula allows us to find the area of an equilateral triangle without directly measuring its height or base.
Perimeter: The perimeter of an equilateral triangle can be found by multiplying the length of one side by three. Since all sides are equal, this shortcut helps us quickly calculate the total distance around the triangle.
Overall, the properties of equilateral triangles make them fascinating and useful shapes to study. Whether it’s calculating their area, solving geometric problems, or exploring their symmetrical nature, equilateral triangles provide a solid foundation for understanding and applying mathematical concepts.
Understanding the characteristics and properties of equilateral triangles
An equilateral triangle is a special type of triangle that has three congruent sides and three congruent angles. It is known for its symmetry and balance, making it a fascinating shape to study in geometry. By understanding its characteristics and properties, we can explore the unique qualities of equilateral triangles and their applications in various fields.
Equal sides: One of the most defining features of an equilateral triangle is that all three sides are equal in length. This means that if we measure any two sides of the triangle, they will be the same length. This property allows equilateral triangles to be used in engineering and construction to create stable and uniform structures.
Equal angles: Equilateral triangles also have three congruent angles, each measuring 60 degrees. This symmetry is not only aesthetically pleasing but also makes equilateral triangles ideal for tessellations and repetitive patterns. The angles of an equilateral triangle make it a central shape in trigonometry and help us calculate various values, such as the sine, cosine, and tangent.
Centroid and incenter: The centroid of an equilateral triangle is the point of intersection of its three medians. It is located two-thirds of the distance from each vertex to the opposite side. The incenter of an equilateral triangle is the center of the inscribed circle, which touches all three sides of the triangle. Both the centroid and incenter have unique properties and play a significant role in geometric constructions and calculations.
Area and perimeter: The area of an equilateral triangle can be determined by using its side length. It can be calculated using various formulas, such as the classic formula A = (√3 / 4) * side^2 or the Heron’s formula. The perimeter, or the total length of the sides, can be found by multiplying the side length by three. These measurements are essential in practical applications, such as calculating material quantities for construction projects.
Application in science and art: Equilateral triangles can be found in various disciplines, from crystallography and molecular structure in science to art and design. They can be used to create intricate patterns, mosaics, and tessellations in visual arts. The balanced and harmonious nature of equilateral triangles has been inspiring artists, architects, and scientists for centuries.
In conclusion, equilateral triangles possess unique characteristics and properties that make them a fascinating subject of study. From their equal sides and angles to the concept of centroids and incenters, equilateral triangles have practical applications in fields like engineering, trigonometry, and construction. Additionally, their aesthetic appeal and presence in art and design highlight the timeless beauty and symmetry of these geometric shapes.
Delving into the Characteristics of Isosceles Triangles

Definition: An isosceles triangle is a type of triangle that has two sides of equal length. In other words, it is a triangle with at least two congruent sides. This distinct property sets isosceles triangles apart from other types of triangles.
Properties: Isosceles triangles possess several unique characteristics. Firstly, the angles opposite the congruent sides are also congruent, making them base angles. These base angles are the angles formed between the two congruent sides. Additionally, the remaining angle, known as the vertex angle, is the angle formed between the non-congruent side and the line segment connecting the midpoints of the two congruent sides.
Isosceles triangles can be classified based on the measures of their angles. If all three angles of the triangle are less than 90 degrees, it is classified as an acute isosceles triangle. Conversely, if one angle measures exactly 90 degrees, it is classified as a right isosceles triangle. Finally, if one angle exceeds 90 degrees, the triangle is classified as an obtuse isosceles triangle.
There are numerous real-life applications of isosceles triangles. Architects and engineers often utilize isosceles triangles when constructing structures with symmetrical designs. Isosceles triangles can also be found in nature, such as in the shapes of certain leaves or petals. Understanding the unique properties and characteristics of isosceles triangles is crucial for solving geometric problems and analyzing various shapes and structures in the real world.
Examining the unique properties and features of isosceles triangles
Isosceles triangles are a fascinating subset of triangles that possess a range of unique properties and features. Understanding these characteristics can help mathematicians and students alike gain a deeper understanding of the world of triangles.
Definition and Visual Representation
An isosceles triangle is a polygon with three sides, two of which are equal in length. This means that the base angles, formed by the base and the two equal sides, are also of equal measure. Visually, an isosceles triangle can be represented as two congruent triangles attached along their equal sides, forming a distinctive V shape.
Properties and Features
- Base and Height: One of the key properties of an isosceles triangle is that it has a base and a corresponding height. The base of the triangle is the side that is not equal in length to the other two sides. The height of the triangle is the perpendicular distance between the base and the vertex opposite the base.
- Angles: Since an isosceles triangle has two equal sides, it also has two equal angles. These two angles are the base angles, which are always congruent. The third angle, opposite the base, is known as the vertex angle.
- Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle is a special case of an isosceles triangle where all three sides and three angles are equal. In other words, an equilateral triangle is an isosceles triangle with congruent sides and congruent angles.
- Isosceles Triangle Theorem: The Isosceles Triangle Theorem states that if two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite those sides are congruent. This property is a valuable tool for solving problems involving isosceles triangles.
- Area and Perimeter: The area of an isosceles triangle can be calculated using the formula A = (b * h) / 2, where b represents the length of the base and h represents the height. The perimeter of an isosceles triangle can be found by simply adding the lengths of all three sides.
Overall, isosceles triangles showcase a variety of interesting properties and features that make them a subject of study and exploration in the field of geometry. Whether it’s understanding their unique angles, calculating their area and perimeter, or utilizing the Isosceles Triangle Theorem, these triangles offer a rich opportunity for mathematical analysis and discovery.